Table Of Content
- A Comprehensive Analysis of Dark Stores, AI Automation, and Last-Mile Delivery Innovation
- Executive Summary
- 1. The Dark Store Revolution: Powering Quick Commerce at Scale
- 1.1 Market Dynamics and Strategic Importance
- 1.2 Economic Impact and Hyperlocal Delivery Economics
- 1.3 Technology Innovations in Dark Store Operations
- 1.4 Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
- 2. Hyperlocal Delivery Economics and Last-Mile Innovation
- 2.1 AI and Automation in Route Optimization
- 2.2 Drone Delivery: From Pilots to Scaled Operations
- 2.3 Sustainable Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
- 3. Warehouse Automation and Robotics Revolution
- 3.1 Technology Adoption and Market Dynamics
- 3.2 Core Automation Technologies
- 3.3 Economic Impact and Efficiency Gains
- 3.4 Government Infrastructure Initiatives
- 4. Freight Tech and Logistics Cost Optimization
- 4.1 Digital Freight Platforms and Market Transformation
- 4.2 AI and Big Data Analytics for Demand Forecasting
- 4.3 Integration with Traditional Logistics
- 4.4 Modal Shift and Multimodal Integration
- 5. Key Drivers and Market Outlook 2025-2030
- 5.1 Market Growth Projections and Investment Trends
- 5.2 Competitive Landscape and Strategic Positioning
- 5.3 Strategic Partnerships and Innovation Ecosystem
- 5.4 Sustainability Trends and Green Logistics
- 5.5 Government Policy and Infrastructure Investments
- 6. Future Outlook: The Road to 2030
- 6.1 Technological Convergence
- 6.2 Workforce Transformation
- 6.3 Urban Logistics Transformation
- 6.4 Challenges and Risk Factors
- 7. Strategic Imperatives for Stakeholders
- 7.1 For E-Commerce and Quick Commerce Companies
- 7.2 For Logistics Service Providers
- 7.3 For Technology Providers and Startups
- 7.4 For Policymakers and Regulators
- 8. Case Studies: Excellence in Execution
- 8.1 Reliance Retail: Omnichannel Logistics Mastery
- 8.2 Delhivery: Technology-Driven Logistics Giant
- 8.3 Airbound: Revolutionary Drone Delivery
- 8.4 BigBasket: Grocery E-Commerce to Quick Commerce Transformation
- 9. Sector-Specific Deep Dive: Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics
- 9.1 Cold Chain Market Dynamics
- 9.2 Pharmaceutical Logistics Excellence
- 10. Conclusion: Navigating the Logistics Revolution
- About This Report
- About Webverbal Research
A Comprehensive Analysis of Dark Stores, AI Automation, and Last-Mile Delivery Innovation
Market Overview: India’s logistics sector stands at USD 349.37 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 545.56 billion by 2030, expanding at a 9.32% CAGR. This transformation is powered by revolutionary technologies in AI, robotics, and hyperlocal delivery infrastructure.
Executive Summary
India’s logistics and supply chain ecosystem is experiencing an unprecedented technological revolution, driven by the explosive growth of quick commerce, sophisticated warehouse automation, and AI-powered delivery networks. With logistics costs targeted to decrease from 13-14% of GDP to single digits by 2030, the sector is embracing dark stores, autonomous delivery systems, and intelligent warehouse robotics at scale. This report examines the critical innovations reshaping India’s logistics landscape from 2025 to 2030, with comprehensive data on market dynamics, technological adoption, and strategic imperatives.
Key Market Indicators (2025-2030):
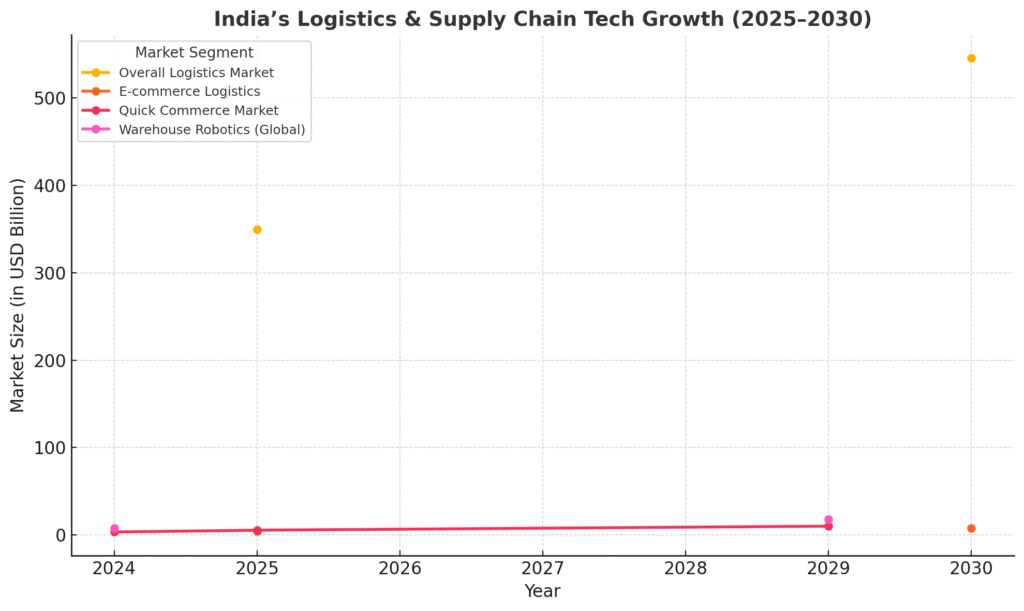
- Overall Logistics Market: USD 349.37B (2025) → USD 545.56B (2030) at 9.32% CAGR
- E-commerce Logistics: USD 4.42B (2025) → USD 7.85B (2030) at 12.18% CAGR
- Quick Commerce Market: USD 3.34B (2024) → USD 5-5.38B (2025) → USD 10B (2029)
- Warehouse Robotics (Global): USD 7.93B (2024) → USD 17.91B (2029) at 17.70% CAGR
1. The Dark Store Revolution: Powering Quick Commerce at Scale
1.1 Market Dynamics and Strategic Importance

Dark stores—mini-warehouses exclusively designed for online order fulfillment—have emerged as the cornerstone of India’s quick commerce revolution. Unlike traditional retail outlets, these facilities are optimized for speed, operating as automated fulfillment centers strategically located in high-density urban areas to enable 10-30 minute deliveries.
Operational Scale of Major Players (2025):
- Reliance Retail (JioMart): 600+ dark stores operational (Q3 2024), covering 5,000 pin codes across 1,000 cities. JioMart logged 42% Q-o-Q growth and 200%+ Y-o-Y growth in average daily orders. The retail giant has extended 30-minute delivery to electronics and accessories across 10 cities.
- Flipkart Minutes: Operating 120-150 dark stores as of March 2025, targeting 500-550 by Big Billion Days 2025. The platform expanded to 300 dark stores by March 2025, positioning itself as the fourth-largest quick commerce player.
- BigBasket (BB Now): Targeting 600-900 dark stores to dominate the quick commerce segment. BB Now accounts for over 50% of BigBasket’s total sales, with plans to generate USD 1 billion of the projected USD 1.5 billion in FY2025 revenue through quick commerce services.
- Blinkit (Zomato): Market leader with USD 3.7 billion annualized gross sales run rate, supported by an extensive dark store network across metro cities.
- Zepto: USD 3 billion annualized run rate, optimizing operations where orders are ready for pickup within seconds of placement.
- Swiggy Instamart: USD 1.8 billion annualized run rate, actively expanding dark store presence with real estate consultancies.
- Ola Dash: Announced plans for 500 dark stores across 20 cities (2022 targets), though actual implementation has faced challenges.
Quick Commerce Market Trajectory: According to BofA Securities, the quick commerce market is projected to grow from USD 21 billion (current) to USD 31 billion by FY27 under a bullish scenario, expanding retail market share from 1.7% to 2.4%.
As India’s logistics and retail sectors evolve, the next wave of disruption is unfolding in hyperlocal commerce. To understand how ultra-fast delivery players are scaling beyond metros, explore Quick Commerce India 2025: Zepto, Blinkit & BigBasket’s Race Into Tier-3 Bharat — a deep dive into how India’s quick commerce revolution is moving into Bharat’s Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
1.2 Economic Impact and Hyperlocal Delivery Economics
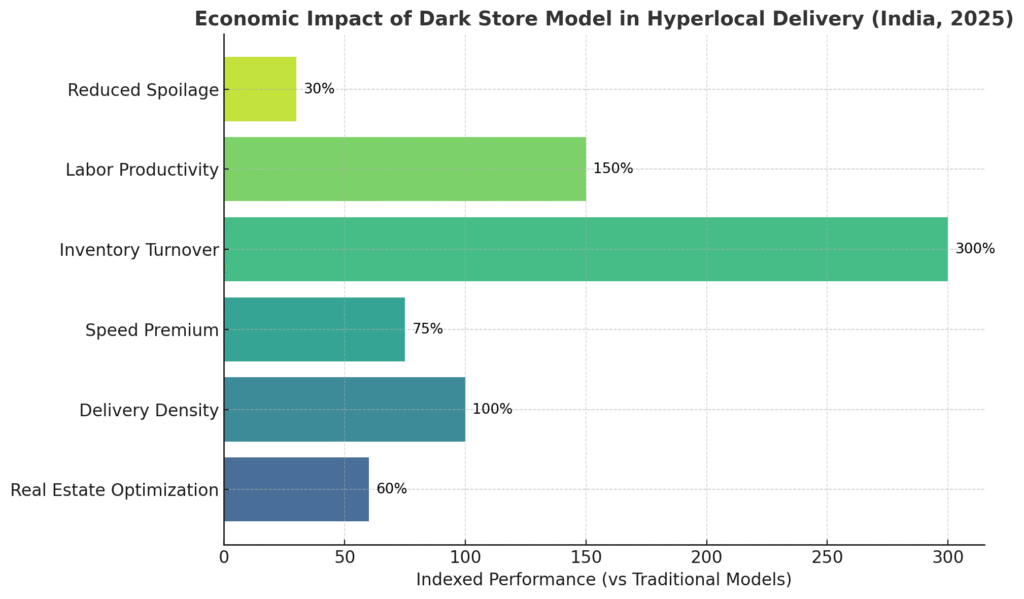
Dark stores fundamentally transform last-mile economics through:
Cost Efficiency Metrics:
- Real Estate Optimization: Dark stores operate at 2,000-5,000 sq ft facilities in high-density areas, requiring significantly lower investment than traditional retail
- Primary Expenses: Rent, utilities, and staff salaries typically don’t exceed a small fraction of revenue
- Delivery Density: Enables 60+ deliveries per day per delivery partner versus 30 for traditional models
- Speed Premium: 10-minute urban deliveries versus 30-40 minute traditional routes drive higher customer acquisition costs but superior lifetime value
Economic Advantages:
- Inventory Turnover: 3x faster than traditional warehouses due to focused SKU selection and demand-driven stocking
- Labor Productivity: 40-60% improvement through warehouse automation and optimized picking processes
- Reduced Spoilage: Real-time inventory management cuts perishable goods wastage by 25-30%
1.3 Technology Innovations in Dark Store Operations
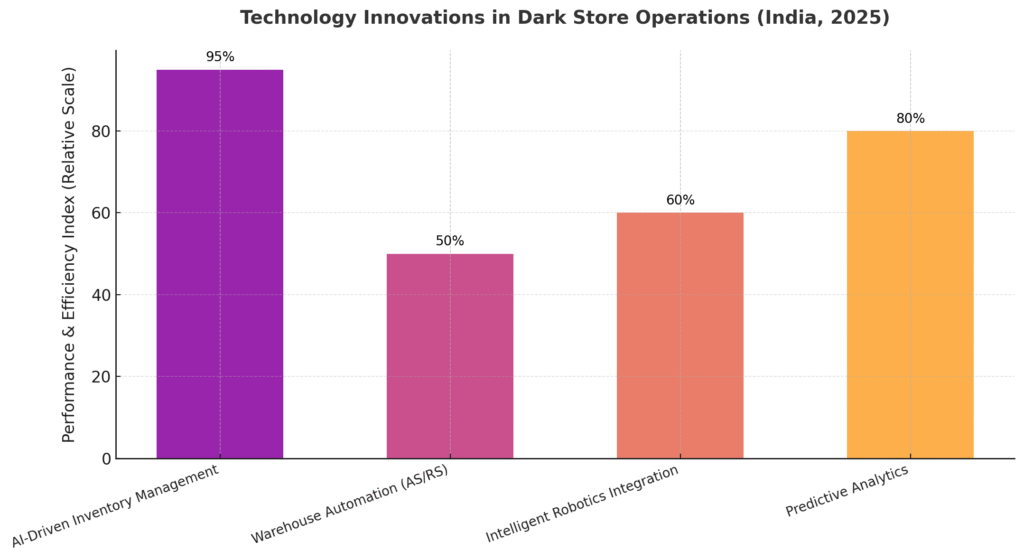
AI-Driven Inventory Management: Dark stores leverage sophisticated demand forecasting algorithms that analyze:
- Historical purchase patterns and seasonal trends
- Real-time local events and weather conditions
- Competitive pricing and promotion impact
- Micro-market demographic preferences
This enables predictive stocking that maintains 95%+ order fulfillment rates while minimizing overstocking costs.
Warehouse Automation Technologies:
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS):
- Retrieve goods 3x faster than manual systems
- Reduce order fulfillment time by 40-50%
- Enable vertical storage optimization in limited urban spaces
Intelligent Robotics Integration:
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) navigate dynamic warehouse environments without fixed infrastructure
- AI-powered vision systems automate sorting, picking, and placing tasks
- Collaborative robots work alongside human workers, handling repetitive tasks while humans manage exceptions
Predictive Analytics:
- IoT sensors track real-time inventory levels, temperature, and storage conditions
- RFID-enabled inventory tracking improves warehouse accuracy and speeds up audits
- Machine learning models predict peak demand periods, enabling proactive staffing and stock positioning
BigBasket’s Technology Edge: BB Now integrates AI-powered inventory systems ensuring product availability while leveraging its subscription service (BB Star) to provide discounts and priority delivery for frequent shoppers. The platform seamlessly integrates with BigBasket’s main e-commerce ecosystem, enabling customers to switch between scheduled and rapid orders.
1.4 Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Urban Real Estate Costs:
- Challenge: Premium urban locations command high rental rates, impacting profitability
- Mitigation: Strategic partnerships with real estate developers for dedicated logistics spaces; government incentives under National Logistics Policy for Grade A warehousing facilities; vertical expansion using multi-story dark stores
Operational Complexities:
- Challenge: Managing inventory across hundreds of micro-warehouses with varying demand patterns
- Mitigation: Centralized AI-powered demand forecasting platforms; automated inter-dark store transfer systems; dynamic pricing algorithms to balance inventory
Last-Mile Delivery Challenges:
- Challenge: Urban congestion and traffic unpredictability affecting delivery promise times
- Mitigation: AI route optimization accounting for real-time traffic; deployment of e-bikes and two-wheelers for narrow lane access; establishment of delivery pods in gated communities and commercial complexes
Regulatory Compliance:
- Challenge: Food safety regulations, labor laws, and municipal zoning restrictions
- Mitigation: Automated compliance monitoring systems; strategic engagement with local authorities; investment in cold chain infrastructure for temperature-sensitive products
2. Hyperlocal Delivery Economics and Last-Mile Innovation

2.1 AI and Automation in Route Optimization
Modern hyperlocal delivery systems leverage sophisticated AI algorithms to optimize every aspect of the delivery journey:
Dynamic Route Planning:
- Real-Time Traffic Integration: Systems analyze live traffic data, road closures, and congestion patterns to calculate optimal routes
- Multi-Stop Optimization: AI algorithms solve complex traveling salesman problems, batching multiple orders along efficient delivery corridors
- Delivery Time Slot Prediction: Machine learning models predict accurate delivery ETAs with 95% accuracy, accounting for historical patterns and current conditions
Cost Reduction Metrics:
- Fuel Efficiency: AI-optimized routing reduces fuel consumption by 15-20%
- Delivery Density: Intelligent batching increases deliveries per hour by 30-40%
- Failed Delivery Reduction: Predictive analytics for customer availability reduces failed deliveries by 25%
Leading Implementations: Companies like Delhivery, Shadowfax, and Dunzo have implemented AI-driven logistics platforms that process billions of data points daily, achieving:
- 40% more orders processed per hour
- 99.8% picking accuracy through computer vision systems
- 25% reduction in delivery times across operations
2.2 Drone Delivery: From Pilots to Scaled Operations
India’s drone delivery ecosystem is rapidly maturing, supported by progressive regulatory frameworks and strategic industry partnerships.
Regulatory Framework (Drone Rules 2021 & 2023 Amendments):
- Airspace Classification: 86% of India’s airspace designated as green zones (no permission required for operations)
- Registration: Digital Sky platform enables streamlined drone registration and flight permissions
- BVLOS Operations: Beyond Visual Line of Sight operations permitted under experimental exemptions, with expanding corridors
Government Initiatives:
- PLI Scheme for Drones (2021): ₹120 crore allocated to boost private drone manufacturing
- Drone Shakti Initiative: Promoting drone-as-a-service (DaaS) in agriculture and infrastructure
- BVLOS Pilot Projects: Testing drones for logistics and long-range delivery across multiple states
- Drone Manufacturing Growth: Expected to grow from ₹60 crore (2020-21) to over ₹900 crore (FY 2023-24)
Operational Trials and Partnerships:
Skye Air Mobility:
- Key player in drone logistics for last-mile deliveries
- Partnerships with BigBasket, DTDC, Dunzo, Flipkart Health+, and Tata 1mg
- Completed first drone delivery of 7.5 km in 3-4 minutes (versus 15 minutes by road)
- Uses smart technology to optimize routes, skip traffic, and reduce delivery costs
DTDC Express:
- Launched drone-based deliveries through Skye Air partnership
- Plans to expand drone delivery service to strategic locations across India
- Focus on eco-friendly logistics cutting carbon emissions and traffic congestion
Medicine from the Sky Project:
- Operating in Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, and Nagaland
- Delivering medical supplies to remote, hard-to-reach terrains
- Training local youth including India’s first female drone pilots
- Demonstrating viable use cases for emergency healthcare logistics
TechEagle:
- Focused on healthcare, e-commerce, hyperlocal, and last-mile logistics
- Working with government departments and private enterprises
- Targeting impact on a billion lives through On-Demand Drone Delivery network
Airbound (Y-Combinator backed):
- Raised USD 8.65 million in 2025 to build rocket-like drones for one-cent deliveries
- Pilot program with Narayana Health in Bengaluru for medical logistics
- Targeting 10 deliveries per day of medical tests, blood samples, and critical supplies
- Plans to scale to one million deliveries per day and enter U.S. market within three years
Economic Impact Projections:
- Cost Reduction: Drone deliveries can cut shipping costs by up to 50% over time
- Speed Advantage: Urban deliveries completed in under 10 minutes versus 30-40 minutes by road
- Delivery Capacity: Drones can deliver up to 60 orders daily versus 30 for traditional delivery partners
- Global Investment: Drone investments surpassing ₹421.90 billion globally in the last decade
World Economic Forum Projection: Last-mile deliveries will grow by 78% by 2030 due to the e-commerce boom, positioning drones as critical infrastructure.
2.3 Sustainable Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
Electric Vehicle Adoption:
- Union Budget 2025: Fresh incentives for EV adoption in commercial transportation
- MoEVing Partnership: Strategic alliance with Safexpress to deploy EVs for last-mile deliveries, targeting 100% EV adoption by 2030
- Current Fleet: MoEVing operates over 3,000 EVs across 25 cities
- Environmental Impact: Targeting significant reduction in carbon emissions across logistics ecosystem
E-Bike Deployment:
- Ideal for narrow urban lanes and congested areas
- Lower operational costs compared to motorized vehicles
- Reduced environmental footprint with zero emissions
Green Warehousing:
- Tax deductions for businesses adopting sustainable warehousing solutions
- Use of renewable energy, energy-efficient storage facilities
- Eco-friendly construction materials
- Solar rooftop projects to offset refrigeration energy costs
Sustainability Metrics:
- Cold chain logistics using IoT-enabled temperature control reduces energy waste by 15-20%
- Green corridor initiatives for freight transport
- Focus on carbon-neutral freight corridors
3. Warehouse Automation and Robotics Revolution
3.1 Technology Adoption and Market Dynamics
India’s warehousing sector is undergoing rapid digital transformation, driven by e-commerce expansion, labor challenges, and government incentives.
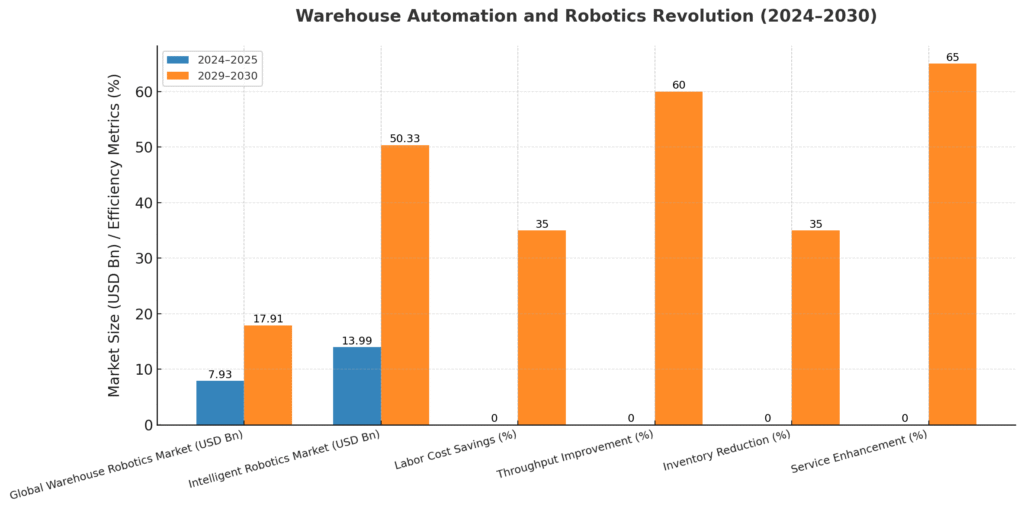
Global Warehouse Robotics Market:
- 2024: USD 7.93 billion
- 2029: USD 17.91 billion
- CAGR: 17.70%
Intelligent Robotics Market:
- 2025: USD 13.99 billion
- 2030: USD 50.33 billion
- CAGR: 29.2%
- Asia Pacific Leadership: Largest market share driven by industrialization in China, Japan, South Korea, and India
India-Specific Growth Drivers:
- Quick commerce platforms (Zepto, Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart) requiring ultra-fast fulfillment centers
- Labor shortages and rising costs necessitating automation
- Government incentives through PLI schemes supporting AI, robotics, and supply chain digitalization
- Expansion of e-commerce to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities demanding scalable infrastructure
3.2 Core Automation Technologies
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs):
- Navigate busy warehouse environments without fixed paths or infrastructure
- Optimize routes dynamically, avoid obstacles, and collaborate to minimize congestion
- Reduce material travel time by 30-40% compared to traditional systems
- Enable workers to focus on value-added tasks like exception handling and quality control
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS):
- Retrieve goods 3x faster than manual systems
- Reduce order fulfillment time significantly
- Enable vertical storage optimization in space-constrained facilities
- Reliance Retail leverages AS/RS to quickly replenish stores across India
AI-Powered Robotics:
- Vision Systems: Computer vision enables robots to adapt to complex environments, reducing errors
- 360-Degree LiDAR: Enables autonomous navigation across entire warehouse grids
- High-Speed Operation: Complete pick and put tasks at accelerated rates
- Efficiency Levels: AI-driven robots achieving near 90% operational efficiency
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
- Real-time inventory tracking and management
- Automated order processing and fulfillment
- Integration with IoT sensors and RFID technology
- Predictive maintenance reducing downtime
3.3 Economic Impact and Efficiency Gains
Labor Cost Optimization:
- Savings: Up to 35% reduction in labor costs for routine tasks
- Workforce Redeployment: Workers retrained as robot supervisors, data analysts, and exception managers
- Job Creation: Emerging roles in robotics maintenance, programming, and logistics analysis
- Employee Satisfaction: Companies investing in upskilling report higher retention rates
Operational Efficiency Metrics:
- Throughput Improvement: 40-60% increase in warehouse throughput
- Picking Accuracy: 99.8% accuracy through computer vision systems (Amazon reference)
- Inventory Management: Real-time cycle counting and stock verification by autonomous robots
- Order Processing: Amazon processes 40% more orders per hour with 520,000+ AI-powered robots
Cost Savings:
- AI-Driven Solutions: Cut logistics costs by 15% (McKinsey report)
- Inventory Reduction: Lower inventory levels by 35%
- Service Enhancement: Improve service levels by 65%
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduce equipment downtime through IoT-enabled monitoring
Strategic Investments:
- Delhivery-Falcon Autotech: Delhivery increased stakeholding to 39% in Falcon Autotech, validating automation potential in Indian logistics
- Amazon: USD 40 million investment in robotics innovation hub (2019)
- Honeywell: USD 50 million investment in Robotics Innovation Hub (2019)
3.4 Government Infrastructure Initiatives
PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan:
- Launch: October 2021 as integrated digital platform
- Integration: 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs on 1,700-layer GIS platform
- Project Assessment: 208 major infrastructure projects worth ₹15.39 lakh crore evaluated
- Infrastructure Projects: 434 projects worth ₹11.17 lakh crore identified to enhance logistics efficiency
- Target: Improve India’s World Bank Logistics Performance Index ranking from 38th to top 25 by 2030
Key Achievements:
- Road Transport: 8,891 kilometers of roads planned using Gati Shakti platform
- Railways: 27,000+ kilometers of railway lines planned under National Master Plan
- Final Location Surveys: Increased from 57 in FY 2021 to 449 in FY 2022
- 5G Deployment: 13 crore subscribers in first year, enhancing real-time tracking and autonomous systems
- Rural Connectivity: 41,000+ mobile towers sanctioned for rural and remote areas
National Logistics Policy (2022):
- Objective: Reduce logistics costs from 13-14% to 8% of GDP by 2030
- Digital Platform: Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) for real-time data access
- E-Logs System: Online issue resolution for logistics stakeholders
- ULIP Integration: National Logistics Data Bank tracked over 60 million EXIM containers using RFID and IoT
PLI Scheme for Robotics & AI:
- Government incentives for automation in logistics and warehousing
- Support for local AI and robotics startups
- “Make in India” initiative driving domestic manufacturing
Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):
- Completion Status: 96% operational as of 2024
- Impact: Cutting transit times on trunk routes by up to 65%
- Modal Mix: Improving rail freight share in overall logistics
Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs):
- 35 parks approved across India
- Integrated customs, storage, and transport services
- RFID gate automation and e-delivery orders
- Green-transport incentives for park tenants
4. Freight Tech and Logistics Cost Optimization
4.1 Digital Freight Platforms and Market Transformation
India’s traditionally fragmented freight market is consolidating through digital platforms that aggregate trucking capacity and enable transparent, efficient load matching.
Market Dynamics:
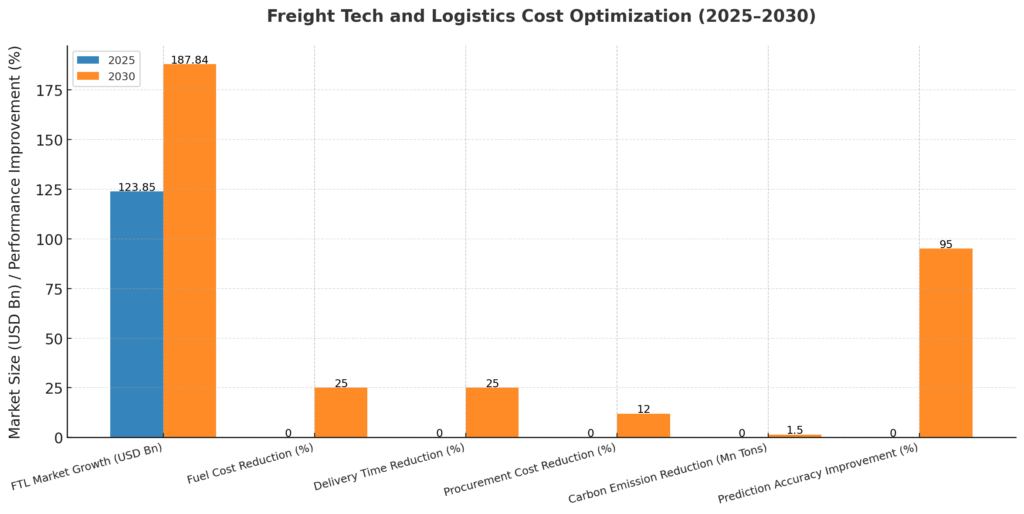
- Full-Truck-Load (FTL) Market: USD 123.85 billion (2025) → USD 187.84 billion (2030) at 8.69% CAGR
- FASTag Penetration: 98% penetration eliminating cash toll queues, generating ₹178 crore (USD 1.28 billion) daily toll receipts—more than doubling FY21 levels
- GST Impact: Hub-and-spoke warehousing model enables 500,000 sq ft single-roof facilities, delivering economies of scale
Digital Freight Platform Capabilities:
- Real-Time Load Matching: AI algorithms match available freight with truck capacity in real-time
- Dynamic Pricing: Market-driven pricing based on demand, route, and capacity availability
- Digital Documentation: Paperless transactions reducing processing time by 50-60%
- Payment Integration: Secure digital payment systems improving cash flow for transporters
- Fleet Management: Telematics and GPS tracking for real-time fleet visibility
Leading Digital Freight Platforms:
- Asset-light operators deploying platforms for payment and fleet-management services
- Aggregating fragmented trucking base, opening fresh revenue pools
- Enabling just-in-time inventory strategies for e-commerce and quick commerce
4.2 AI and Big Data Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Predictive Demand Forecasting:
- AI models analyze past sales, seasonality, and market trends to forecast demand
- Prevent overstocking and stockouts through precise inventory positioning
- Enable proactive capacity planning and resource allocation
Route Optimization at Scale:
- Calculate most efficient delivery routes considering traffic, weather, and road conditions
- Reduce fuel costs and delivery time by 15-25%
- Enable complex round-trip routing increasing driver home-time and reducing attrition
Real-Time Analytics:
- Process over 10,000 potential manufacturing partners for supplier evaluation
- Identify optimal matches 75% faster than traditional methods
- Reduce procurement costs by average of 12%
Maersk Case Study:
- AI-driven maritime logistics decreased vessel downtime by 30% through predictive maintenance
- Annual savings over USD 300 million
- Reduced carbon emissions by 1.5 million tons
- Analyzes over 2 billion data points daily from 700+ vessels
- Predicts equipment failures up to 3 weeks in advance with 85% accuracy
DHL Performance Metrics:
- AI-powered forecasting platform reduced delivery times by 25% across 220 countries
- Improved prediction accuracy to 95%
- “Smart Trucks” with machine learning algorithms for dynamic rerouting
- Saved 10 million delivery miles annually
4.3 Integration with Traditional Logistics
Technology-Traditional Hybrid Model:
- Digital platforms complementing existing physical infrastructure
- Technology adoption across asset-heavy traditional logistics companies
- Automation-as-a-Service (AaaS) enabling affordable entry for smaller players
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency:
- Warehouses using blockchain platforms for inventory tracking
- Eliminates manual reconciliations and reduces documentation fraud
- Enhanced traceability for temperature-sensitive goods
- Cold storage IoT solutions for vaccine distribution (Serum Institute of India)
IoT Integration:
- Real-Time Tracking: IoT sensors track shipments and supply chain movements
- RFID Technology: Enables faster inventory audits and reduces human errors
- Temperature Monitoring: Sub-±0.5°C variance essential for biologics and pharmaceuticals
- DHL Implementation: IoT sensors and real-time tracking in Indian fulfillment centers ensure temperature-sensitive goods compliance
Digital Twin Technology:
- Virtual replicas of entire supply networks
- Simulate changes and anticipate disruptions before they occur
- Test warehouse layouts and workflows before physical implementation
- Optimize resource allocation and capacity planning
4.4 Modal Shift and Multimodal Integration
Railway Freight Enhancement:
- National Logistics Policy targeting increase in rail freight share from 18% to higher levels
- Dedicated Freight Corridors improving efficiency and capacity
- Reducing road congestion and environmental impact
Waterways Development (Sagarmala Project):
- Modernization of port infrastructure and coastal connectivity
- 9 Indian ports in top 100 ports globally, with Vizag in top 20
- International coastal shipping cargo soared 118% over previous decade
- Inland waterway cargo increased 700% demonstrating viability
Multimodal Logistics Parks:
- Integrated facilities enabling seamless mode switching
- Cross-dock aggregation lifting FTL load factors
- Reduced idle time at loading bays
- Adjacent to ports, airports, and railheads for tighter supply-chain orchestration
5. Key Drivers and Market Outlook 2025-2030
5.1 Market Growth Projections and Investment Trends
Overall Market Trajectory: Multiple research firms project robust growth with slight variations:
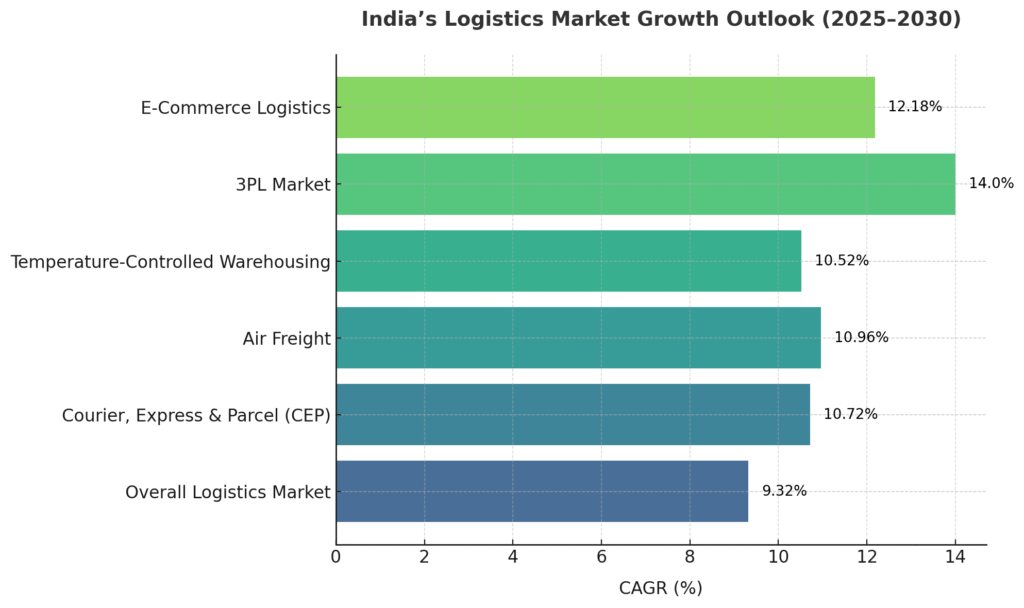
- Mordor Intelligence: USD 349.37B (2025) → USD 545.56B (2030) at 9.32% CAGR
- Grand View Research: USD 228.4B (2024) → USD 357.3B (2030) at 7.7% CAGR
- IMARC Group: USD 228.4B (2024) → USD 428.7B (2033) at 6.50% CAGR
Segment-Specific Growth:
Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP):
- Fastest growing segment at 10.72% CAGR (2025-2030)
- International flows expanding at 11.03% CAGR
- Driven by e-commerce and cross-border trade
Air Freight:
- Fastest-growing transport mode at 10.96% CAGR (2025-2030)
- Led by electronics and pharmaceutical exports
- Investments in bonded warehouses adjacent to airports
Temperature-Controlled Warehousing:
- Growing at 10.52% CAGR (2025-2030)
- Catalyzed by pharma exports and processed food
- IoT telemetry enabling precise temperature control
3PL Market:
- Projected to grow at CAGR over 14% (2025-2033)
- Grade A warehousing demand expected to reach 1.2 billion square feet by 2027
- Cold chain logistics contributing significantly to sector growth
E-Commerce Logistics:
- USD 4.42B (2025) → USD 7.85B (2030) at 12.18% CAGR
- Other functions and value-added services emerging as fastest-growing segment at ~15% (2024-2029)
Private Equity Investment:
- Warehousing & logistics sector captured 66% of private equity investments across all asset classes in H1 2024
- Sector contributes 13-14% to India’s GDP
5.2 Competitive Landscape and Strategic Positioning
Quick Commerce Leaders:
- Zomato (Blinkit): ~58% market share in food and quick commerce; contribution margin positive in 2024
- Swiggy (Instamart): ~42% share; targeting profitability by 2025; broader service portfolio
- Zepto: Dedicated q-commerce player focused on ultra-fast grocery deliveries
- Reliance (JioMart): Largest network with 600+ dark stores, strong tier-2/3 city presence
- Flipkart Minutes: Rapid expansion positioning as fourth-largest player
Top 80% Market Concentration: Swiggy Instamart, Blinkit, Zepto, BigBasket, and Dunzo collectively hold more than 80% quick commerce market share.
Traditional E-Commerce Entry:
- Amazon Fresh and Flipkart Minutes intensifying competition
- Testing 15-minute delivery services in select cities
- Leveraging existing infrastructure and customer base
Logistics Giants:
- Delhivery: India’s largest fully integrated logistics provider
- FedEx, DHL: Global integrators expanding network coverage to 220+ countries
- Mahindra Logistics, Blue Dart, DTDC, Ecom Express: Domestic leaders
- Xpressbees, Shadowfax, Shiprocket: Digital-native logistics platforms
5.3 Strategic Partnerships and Innovation Ecosystem
Recent Strategic Partnerships:
MoEVing-Safexpress (January 2025):
- Strategic partnership promoting sustainable logistics
- Safexpress investment in MoEVing
- Target: 100% EV adoption by 2030
- Leveraging 3,000+ EV fleet across 25 cities
Delhivery-Team Global Logistics (September 2024):
- Significant expansion of cross-border ocean freight capabilities
- Enhanced inbound and outbound routes
Drone Delivery Collaborations:
- Skye Air with BigBasket, DTDC, Dunzo, Flipkart Health+, Tata 1mg
- DroneAcharya partnership with TSAW Drones for BVLOS operations
- TechEagle partnerships with government and private enterprises
Technology Platform Integrations:
- Reliance utilizing FYND and Locus for fulfillment and route optimization
- Integration of Bharat Trade Net with customs and port operations
- ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce) emerging as wildcard with lower commissions
Startup Innovation:
- Airbound: Y-Combinator backed, raised USD 10+ million, revolutionary drone design
- Falcon Autotech: Warehouse automation solutions with Delhivery investment
- TechEagle, DroneAcharya: BVLOS drone delivery specialists
5.4 Sustainability Trends and Green Logistics
Regulatory Push:
- Union Budget 2025 tax deductions for sustainable warehousing solutions
- Incentives for renewable energy adoption in logistics facilities
- Maritime Development Fund of ₹25,000 crore for domestic shipbuilding
Electric Vehicle Transition:
- Commercial fleet electrification with favorable tax benefits and subsidies
- Green warehousing solutions with energy-efficient infrastructure
- Eco-friendly construction materials for logistics facilities
Carbon Footprint Reduction:
- AI-optimized routing reducing fuel consumption by 15-20%
- Drone delivery cutting urban traffic congestion and emissions
- Green corridor initiatives for freight transport
- Solar rooftop projects for warehouse energy independence
Circular Economy:
- Reverse logistics growth (20-25% return rates in fashion)
- Sustainable packaging materials adoption
- Waste reduction through predictive inventory management
5.5 Government Policy and Infrastructure Investments
National Logistics Policy Targets:
- Reduce logistics costs from 13-14% to 8% of GDP by 2030
- Early indicators suggest costs already dropping to ~9%
- Every 1% drop saves billions in trade costs
Infrastructure Investment Pipeline:
- PM Gati Shakti: 434 projects worth ₹11.17 lakh crore
- Maritime Development Fund: ₹25,000 crore
- Dedicated Freight Corridors: 96% completion enabling rail freight growth
- 35 Multimodal Logistics Parks across India
Digital Infrastructure:
- ULIP platform for unified logistics data access
- Digital Sky platform for drone operations
- National Geospatial Data Registry (NGDR) for infrastructure planning
- Logistics Data Bank tracking 60+ million EXIM containers
International Connectivity:
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- Sagarmala Project modernizing 9 ports in global top 100
- Enhanced air freight infrastructure for pharma and electronics exports
6. Future Outlook: The Road to 2030
6.1 Technological Convergence
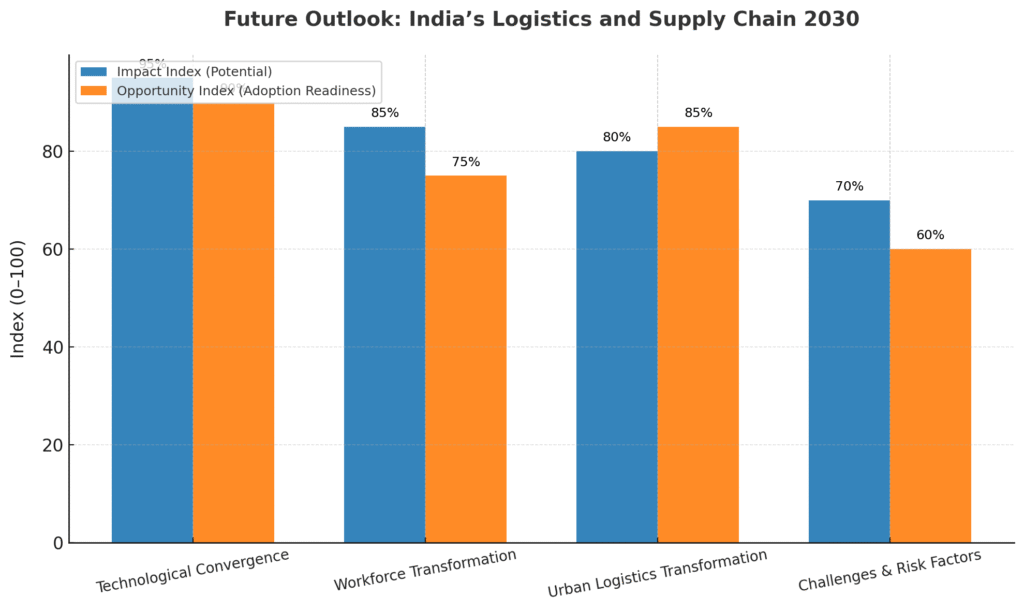
The next five years will witness unprecedented convergence of technologies:
5G and Edge Computing:
- Sub-millisecond response times enabling autonomous vehicles and robotics
- Real-time analytics processing at warehouse and delivery vehicle edge
- Massive IoT device connectivity across supply chain
Generative AI Applications:
- Optimal transportation routes, warehouse layouts, and packaging designs
- Natural language interfaces for supply chain management
- Automated documentation and compliance management
Quantum Computing (Emerging):
- Complex optimization problems in logistics network design
- Advanced cryptography for secure supply chain data
- Real-time simulation of massive supply chain scenarios
6.2 Workforce Transformation
Skills Evolution:
- Traditional logistics roles evolving to technology management
- Growing demand for data analysts, AI specialists, and robotics engineers
- National logistics universities and industry-linked training hubs
Human-Robot Collaboration:
- Cobot (collaborative robot) deployment allowing workers to focus on complex tasks
- Augmented reality glasses for warehouse picking and quality control
- Voice-activated systems for hands-free operations
Upskilling Initiatives:
- Government-industry partnerships for logistics skill development
- Online certification programs for warehouse automation
- Drone pilot training programs including India’s first female drone pilots
6.3 Urban Logistics Transformation
Smart City Integration:
- Dedicated logistics zones in smart cities reducing urban congestion
- Micro-consolidation centers enabling sustainable last-mile delivery
- Underground and aerial delivery corridors (long-term vision)
Regulatory Evolution:
- Zoning reforms accommodating dark stores in residential areas
- Standardized drone delivery corridors across metro cities
- Dynamic road pricing incentivizing off-peak deliveries
Consumer Behavior:
- Quick commerce becoming baseline expectation, not premium service
- Sustainability consciousness driving preference for green delivery options
- Subscription models for regular deliveries reducing per-order costs
6.4 Challenges and Risk Factors
Profitability Pressures:
- Quick commerce companies face continued pressure to achieve sustainable unit economics
- Heavy discounting and customer acquisition costs impacting margins
- Need for operational efficiency improvements to offset growth investments
Infrastructure Constraints:
- Urban real estate availability and costs in prime locations
- Last-mile connectivity in tier-2 and tier-3 cities
- Power supply reliability for automated warehouses and cold chain
Cybersecurity Risks:
- Connected supply chains vulnerable to cyberattacks
- Data privacy concerns with extensive customer and operational data
- Need for robust security protocols and compliance frameworks
Regulatory Uncertainty:
- Evolving labor laws impacting gig economy delivery partners
- Data localization requirements affecting cloud-based platforms
- Environmental regulations on packaging and vehicle emissions
Competition Intensity:
- Market consolidation likely as smaller players struggle with profitability
- International giants (Amazon, Alibaba) intensifying competition
- ONDC potentially disrupting commission-based business models
7. Strategic Imperatives for Stakeholders
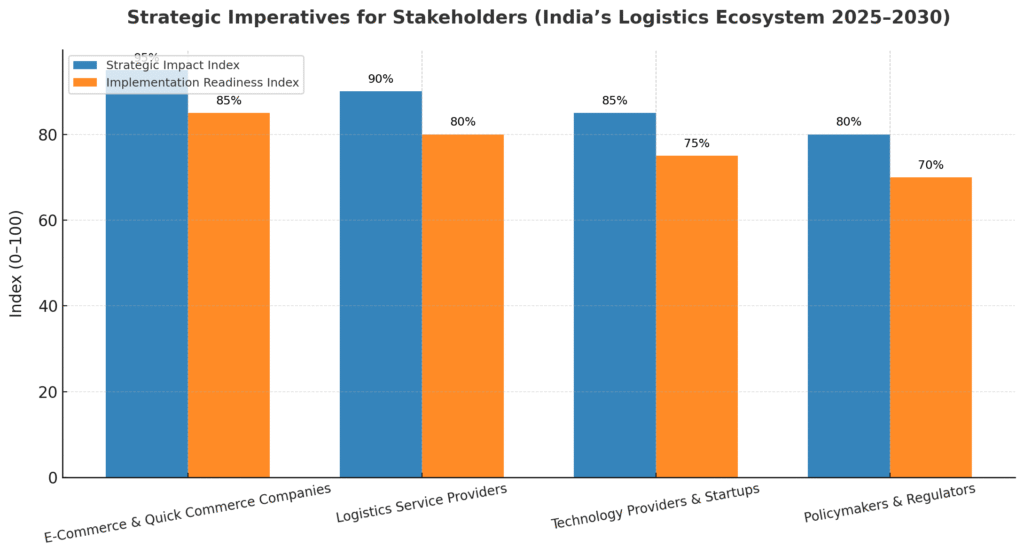
7.1 For E-Commerce and Quick Commerce Companies
Technology Investment Priorities:
- AI-powered demand forecasting to optimize inventory across dark store networks
- Warehouse automation for 40-60% throughput improvements
- Multi-modal delivery networks combining vehicles, drones, and alternative transport
Operational Excellence:
- Dark store location optimization using geospatial analytics
- Supplier relationship management for consistent product availability
- Dynamic pricing algorithms balancing demand and profitability
Sustainability Integration:
- EV fleet transition with target timelines
- Sustainable packaging alternatives
- Carbon footprint tracking and reduction targets
7.2 For Logistics Service Providers
Digital Transformation:
- Investment in WMS, TMS, and integrated logistics platforms
- IoT-enabled fleet management and cargo tracking
- Blockchain for supply chain transparency
Capability Building:
- Specialized services for temperature-controlled logistics
- Cross-border logistics expertise for EXIM growth
- Value-added services (kitting, labeling, returns management)
Partnership Strategies:
- Strategic alliances with e-commerce platforms
- Technology partnerships with robotics and AI providers
- Government collaboration on infrastructure projects
7.3 For Technology Providers and Startups
Innovation Focus Areas:
- Affordable automation solutions for mid-sized warehouses
- India-specific route optimization accounting for infrastructure challenges
- Energy-efficient cold chain solutions
- Drone delivery systems optimized for Indian airspace and regulations
Go-to-Market Strategies:
- Pilot programs with logistics leaders demonstrating ROI
- AaaS (Automation as a Service) models reducing upfront investment
- Integration capabilities with existing systems
Funding and Scaling:
- Leveraging government PLI schemes and startup incentives
- Strategic partnerships with established logistics players
- International expansion leveraging India-developed solutions
7.4 For Policymakers and Regulators
Infrastructure Development:
- Accelerate completion of Multimodal Logistics Parks
- Expand dedicated freight corridors to secondary routes
- Invest in last-mile connectivity in tier-2 and tier-3 cities
Regulatory Frameworks:
- Progressive drone regulations enabling scaled commercial operations
- Standardized guidelines for dark stores and micro-warehouses
- Labor regulations balancing worker protection with industry flexibility
Incentive Structures:
- Extended PLI schemes for logistics technology adoption
- Tax benefits for green logistics infrastructure
- Support for logistics startups and innovation hubs
Skill Development:
- National logistics skill development programs
- University-industry partnerships for supply chain education
- Certification programs for emerging technologies
8. Case Studies: Excellence in Execution
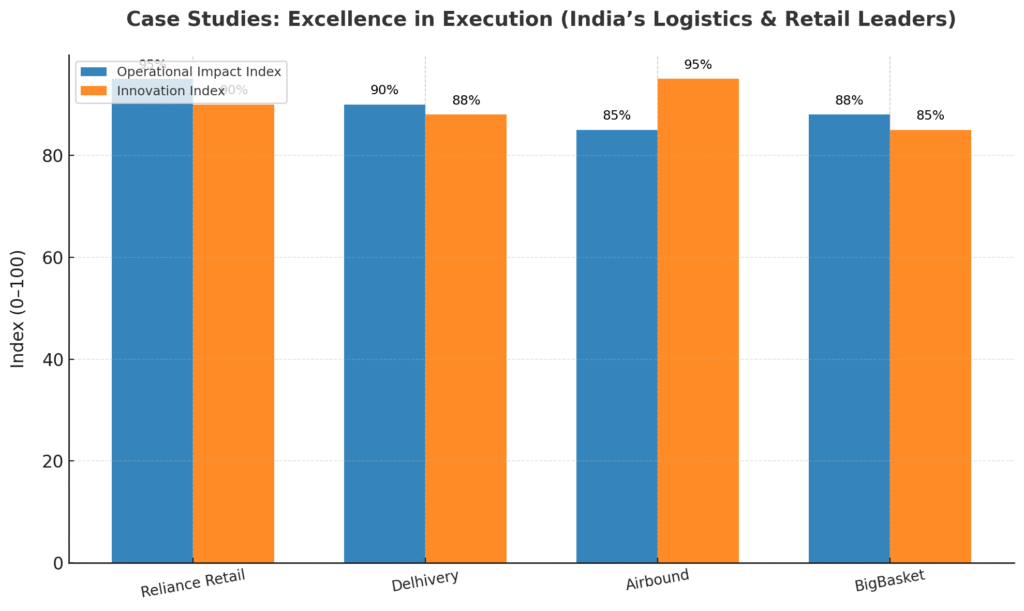
8.1 Reliance Retail: Omnichannel Logistics Mastery
Network Scale:
- 600+ dark stores across 1,000 cities covering 5,000 pin codes
- Seamless integration of online and offline retail networks
- Extended 30-minute delivery to electronics and accessories
Technology Integration:
- FYND platform for inventory visibility across channels
- Locus for intelligent route optimization
- AS/RS for rapid store replenishment
Performance Metrics:
- 42% Q-o-Q growth in average daily orders
- 200%+ Y-o-Y growth demonstrating scalability
- Over 50% JioMart sales through quick commerce (BB Now equivalent positioning)
Strategic Advantage:
- Deep penetration in tier-2 and tier-3 cities leveraging Reliance’s retail footprint
- Cross-selling across grocery, fashion, electronics, and services
- Financial strength enabling sustained investment in infrastructure
8.2 Delhivery: Technology-Driven Logistics Giant
Scale and Reach:
- India’s largest fully integrated logistics provider
- 85+ fulfillment centers and sortation facilities
- 3,500+ partner centers nationwide
Technology Investments:
- 39% stake in Falcon Autotech for warehouse automation
- Proprietary route optimization and network planning algorithms
- Advanced analytics processing millions of shipments daily
Innovation Leadership:
- Strategic partnership with Team Global Logistics for ocean freight
- Cross-border capabilities expansion
- Investment in alternative delivery technologies
8.3 Airbound: Revolutionary Drone Delivery
Innovation Breakthrough:
- Y-Combinator backed with USD 10+ million funding
- Revolutionary rocket-like drone design targeting one-cent deliveries
- Pilot with Narayana Health demonstrating medical logistics viability
Scaling Vision:
- From 10 deliveries per day to one million deliveries per day
- India market expansion followed by U.S. entry within three years
- Medical logistics as initial use case demonstrating critical impact
Technology Differentiation:
- Cost efficiency enabling massive scaling
- Regulatory compliance and safety systems
- Strategic hospital partnerships validating use cases
8.4 BigBasket: Grocery E-Commerce to Quick Commerce Transformation
Business Model Evolution:
- Over 50% of total sales through BB Now quick commerce
- Target of USD 1 billion from USD 1.5 billion FY2025 revenue via quick commerce
- Seamless integration between scheduled and rapid deliveries
Network Expansion:
- Targeting 600-900 dark stores for market dominance
- AI-powered inventory management ensuring high availability
- BB Star subscription model driving customer loyalty
Operational Excellence:
- Strategic partnerships with Skye Air for drone delivery pilots
- Technology partnerships for automation and route optimization
- Focus on fresh produce and perishables differentiating from competitors
9. Sector-Specific Deep Dive: Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics
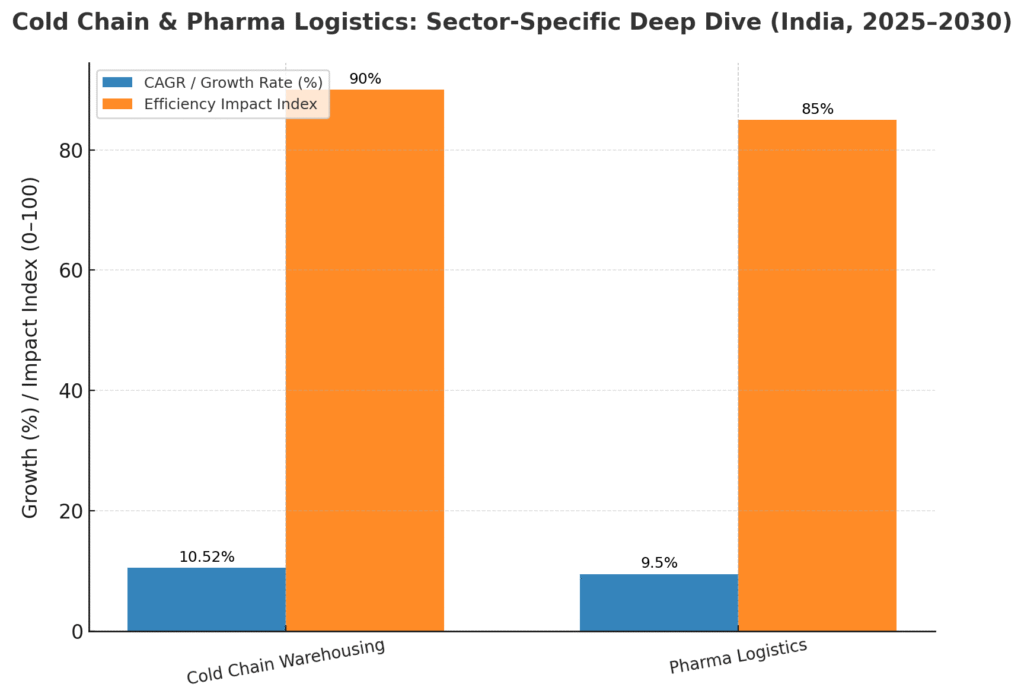
9.1 Cold Chain Market Dynamics
Market Size and Growth:
- Temperature-controlled warehousing growing at 10.52% CAGR (2025-2030)
- Driven by pharmaceutical exports and processed food demand
- Critical for vaccine distribution and biologics
Technology Integration:
- IoT sensors maintaining ±0.5°C temperature variance
- Real-time monitoring and alert systems
- Blockchain for end-to-end cold chain integrity verification
Infrastructure Development:
- Cold storage capacity expansion in proximity to production clusters
- Solar-powered refrigeration reducing operational costs
- Multi-temperature zone warehouses for diverse product requirements
9.2 Pharmaceutical Logistics Excellence
Regulatory Compliance:
- GDP (Good Distribution Practices) certification requirements
- Track and trace systems for anti-counterfeiting
- Temperature excursion documentation for regulatory submissions
Technology Solutions:
- DHL’s temperature-sensitive goods tracking in Indian fulfillment centers
- Drone delivery for emergency medical supplies to remote areas
- Automated inventory management for expiry date tracking
Economic Impact:
- Enabling India’s position as “Pharmacy of the World”
- Supporting vaccine exports and biologics manufacturing
- Reducing medicine spoilage through precise temperature control
10. Conclusion: Navigating the Logistics Revolution
India’s logistics and supply chain technology revolution represents one of the most significant economic transformation opportunities of the decade. The convergence of dark store networks, AI-powered automation, drone delivery systems, and intelligent freight platforms is fundamentally reshaping how goods move across the country.
Key Takeaways:
Market Scale and Growth: The sector’s projected growth from USD 349 billion to USD 545 billion by 2030 represents not just quantitative expansion but qualitative transformation. Quick commerce alone is scaling from USD 3.34 billion to USD 10 billion, demonstrating the velocity of change.
Technology as Competitive Advantage: Companies achieving 40-60% throughput improvements through warehouse automation, 35% labor cost savings, and 15-20% fuel efficiency gains through AI optimization are establishing insurmountable competitive advantages. Technology investment is no longer optional—it’s existential.
Infrastructure and Policy Alignment: PM Gati Shakti’s ₹11.17 lakh crore pipeline, combined with the National Logistics Policy’s target of reducing costs to 8% of GDP, creates a supportive ecosystem for innovation. Early indicators suggest logistics costs dropping to 9%, validating the policy framework.
Sustainability Imperative: The transition to electric vehicles, drone delivery reducing urban congestion, and green warehousing solutions addresses both regulatory requirements and consumer preferences. Companies integrating sustainability into their core strategy will command premium valuations.
Workforce Evolution: The transformation creates both challenges and opportunities in workforce development. While automation reduces routine labor, it creates higher-value roles in technology management, data analytics, and strategic planning. Proactive upskilling will be critical.
Profitability Pathway: The sector must navigate the tension between growth and profitability. Blinkit achieving contribution margin positivity in 2024 demonstrates viable unit economics are achievable. Operational excellence through technology becomes the key differentiator.
Global Competitiveness: India’s logistics innovation, particularly in quick commerce and drone delivery, positions the country as a global innovation hub. Technologies developed for Indian conditions have worldwide applicability, creating export opportunities beyond just logistics services.
The Road Ahead:
The 2025-2030 period will determine which companies and business models achieve sustainable leadership. Success will require:
- Continued aggressive technology investment
- Operational discipline balancing growth and profitability
- Strategic partnerships leveraging complementary strengths
- Regulatory engagement ensuring progressive frameworks
- Sustainability integration as core strategy
- Workforce development preparing for technology-driven operations
India’s logistics sector stands at an inflection point where technology, infrastructure, policy, and market demand align to enable transformational change. Stakeholders who move decisively to capture this opportunity will shape the economy’s future, while those who hesitate risk obsolescence in an increasingly digital, automated, and customer-centric logistics landscape.
The revolution is not coming—it is here. The question is not whether to transform, but how quickly and effectively to execute the transformation.
About This Report
Author Credentials: This analysis synthesizes data from leading industry research firms (Mordor Intelligence, Grand View Research, IMARC), company financial reports, government policy documents, and credible news sources including Economic Times, Business Standard, and specialized logistics publications.
Methodology: The report employs comprehensive secondary research, analyzing publicly available data on market size, company operations, technology adoption, and policy frameworks. Financial metrics and growth projections are sourced from multiple research firms to ensure accuracy.
Sources: Key data sources include company announcements from Reliance Retail, Flipkart, BigBasket, Zomato, Swiggy, and Zepto; government publications on PM Gati Shakti and National Logistics Policy; industry reports from Mordor Intelligence, Grand View Research, and specialized logistics research firms; and credible news publications covering India’s logistics sector.
Last Updated: October 2025
Disclaimer: Market projections and company strategies are based on publicly available information as of October 2025. Actual outcomes may vary based on market conditions, competitive dynamics, and execution capabilities.
About Webverbal Research
Webverbal Research is the editorial and insights division of Webverbal, focused on producing trustworthy, data-driven analysis on India’s startup, e-commerce, and digital economy. Every report and insight published under Webverbal Research is built upon verified data sources, government reports, company filings, and on-ground market intelligence interpreted through a strategic founder’s lens.
Our editorial team combines over a decade of experience in entrepreneurship, digital strategy, and market research, ensuring accuracy, neutrality, and clarity. Each article goes through a multi-layer review process for factual consistency and interpretive integrity before publication.
Editorial Note: This publication reflects independent research and editorial judgment by the Webverbal team. While quantitative insights are based on credible industry data and official disclosures, certain interpretations or forecasts are author-driven estimates intended for informational purposes only.
For corrections, data validation, or research collaborations, please contact hello@webverbal.com.




